X Class 10 Physics 📖Electricity in simplify way by JSunil sir 🔭
🪄In JSunil Sir 🪄way
⤵️➡️➡️➡️➡️⬆️⬆️↩️⤵️
#Electricity is like magic ✨ that #powers our world. It's the flow of tiny particles called electrons through wires and circuits.
👉Let's break it down into simple bits:
1. What is Electricity?
Electricity💡♉ is the movement of tiny particles called electrons . Imagine them like little energy carriers that flow through materials, making things work.
2. Circuits and Pathways
Think of circuits like a path for the electrons to travel. A circuit needs three things: a power🪫 source (like a battery), a pathway (wires), and something to use the electricity (a bulb or device).
3. Current ⚡and Voltage🔋
Current is the flow of electrons in a circuit, and voltage is the "push" that makes them move. It's like water flowing in a river (current) because of the slope (voltage).
4. Conductors ➰and Insulators 🎱
Materials are either good conductors (let electrons flow easily) or insulators (block electron flow). Metals are conductors, and plastic or rubber are insulators.
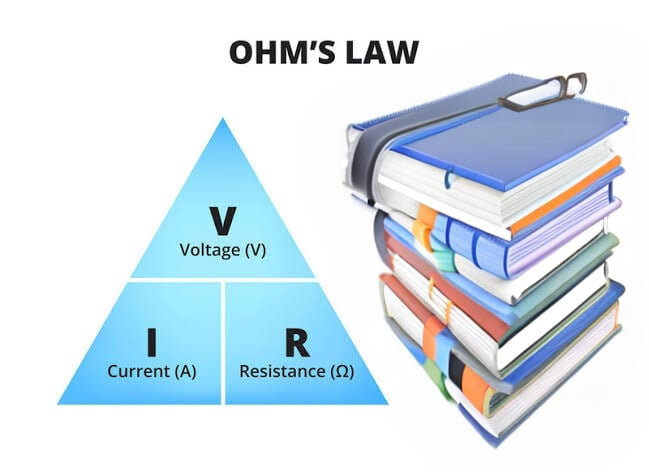
5. Ohm's Law
Ohm's Law tells us that current (I) is equal to voltage (V) divided by resistance (R). Think of it as a traffic rule: current depends on voltage and resistance.
6. Series and Parallel Circuits
In a series circuit, devices are connected one after the other. If one goes out, they all do. In a parallel circuit, devices are like friends; if one stops, others keep going.
7. Safety First
Electricity can be dangerous, so we need safety rules. Avoid touching wires, use switches, and never play near electrical stuff without supervision.
8. Power and Energy
Power is how fast electricity works, and energy is how much it uses. It's like a race (power) and how far you run (energy).
9. Electric Bills
Electricity is not free. You pay for how much energy you use. So, turn off lights and devices when not needed to save energy and money.
➡️ Remember, electricity is a fascinating force ♉ that surrounds us.
By understanding these basics, you'll be able to use and respect electricity safely and even fix simple problems. Stay curious and keep exploring the electrifying world around you!
Fore more details visit my website 🌐 JSunil Tutorial
Question answer ⁉️ of Board Exam question paper
10th Electricity – Remember these terms before solving
Numerical problems
Electricity numerical for class 10 CBSE Trend Setter 50 Problems
Happy 😊 Learning!


Comments
Post a Comment